Appendix J. EQ-i 2.0 Danish Norms
This appendix presents the statistical results pertaining to the development of the EQ-i 2.0 Danish Norms.
- Table J.1. Age by Gender Distribution of the EQ-i 2.0 Danish Normative Sample
- Table J.2. Geographic Distribution of the EQ-i 2.0 Danish Normative Sample by Region
- Table J.3. Education Level Distribution in the Danish EQ-i 2.0 Normative Sample
- Table J.4. Employment Status Distribution in the EQ-i 2.0 Danish Normative Sample
- Table J.5. Occupation Area Distribution in the EQ-i 2.0 Danish Normative Sample
- Table J.6. Organizational Level Distribution of the EQ-i 2.0 Danish Normative Sample
- Table J.7. Effect Sizes for Gender and Age Effects in the EQ-i 2.0 Danish Normative Sample
- Table J.8. Gender Differences in the EQ-i 2.0 Danish Normative Sample
- Table J.9. Age Differences in the EQ-i 2.0 Danish Normative Sample
- Figure J.1. Histogram of EQ-i 2.0 Total EI Standard Scores in the Danish Normative Sample
- Table J.10. Internal Consistency of EQ-i 2.0 Scales in the Danish Normative Sample
- Table J.11. Correlations Among EQ-i 2.0 Composite Scales in the Danish Normative Sample
- Table J.12. Correlations Among EQ-i 2.0 Subscales in the Danish Normative Sample
Table J.1. Age by Gender Distribution of the EQ-i 2.0 Danish Normative Sample
The following table presents the distribution of the EQ-i 2.0 Danish normative sample, categorized by age group and gender. An equal number of men and women were sampled at each age group.
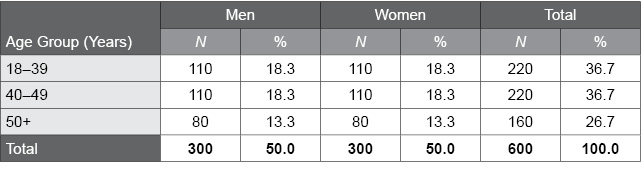
Table J.2. Geographic Distribution of the EQ-i 2.0 Danish Normative Sample by Region
The following table presents the geographic distribution for the EQ-i 2.0 Danish normative sample by region.
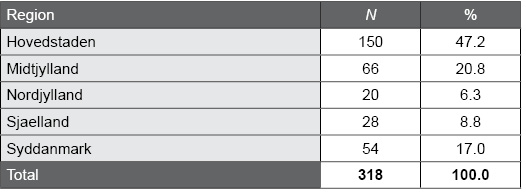
Table J.3. Education Level Distribution in the Danish EQ-i 2.0 Normative Sample
The following table summarizes the education level distribution of the EQ-i 2.0 Danish normative sample. Most applications of the EQ-i 2.0 in Denmark (and in other countries) are within professional contexts; as such, most of the data were collected from individuals with higher education levels.
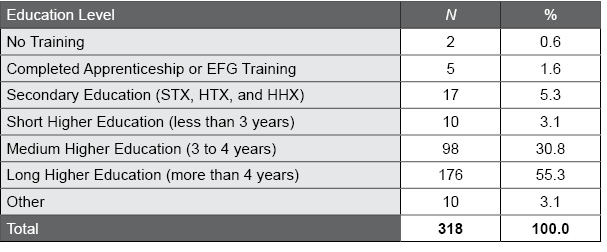
Table J.4. Employment Status Distribution in the EQ-i 2.0 Danish Normative Sample
The following table summarizes the employment status distribution of the EQ-i 2.0 Danish normative sample.

Table J.5. Occupation Area Distribution in the EQ-i 2.0 Danish Normative Sample
The following table summarizes the occupation area distribution of the EQ-i 2.0 Danish normative sample.
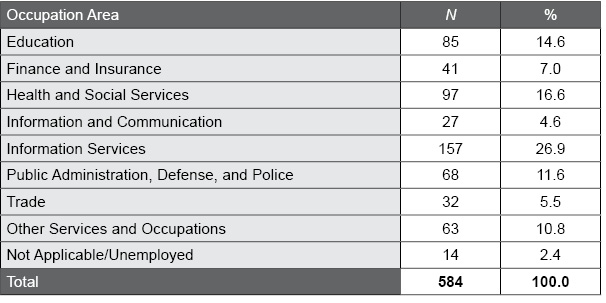
Table J.6. Organizational Level Distribution of the EQ-i 2.0 Danish Normative Sample
The following table summarizes the organizational level distribution of the EQ-i 2.0 Danish normative sample.
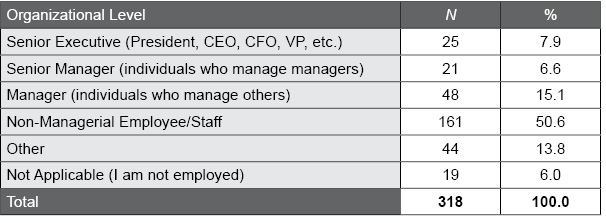
Table J.7. Effect Sizes for Gender and Age Effects in the EQ-i 2.0 Danish Normative Sample
The following table summarizes the effect sizes for the effects of gender and age on the EQ-i 2.0 Total EI score, composite scales, and subscales in the Danish normative sample. Meaningful effect sizes (i.e., |d| ≥ to 0.20, partial η2 ≥ .01) suggest important differences among participants based on the demographic variable.
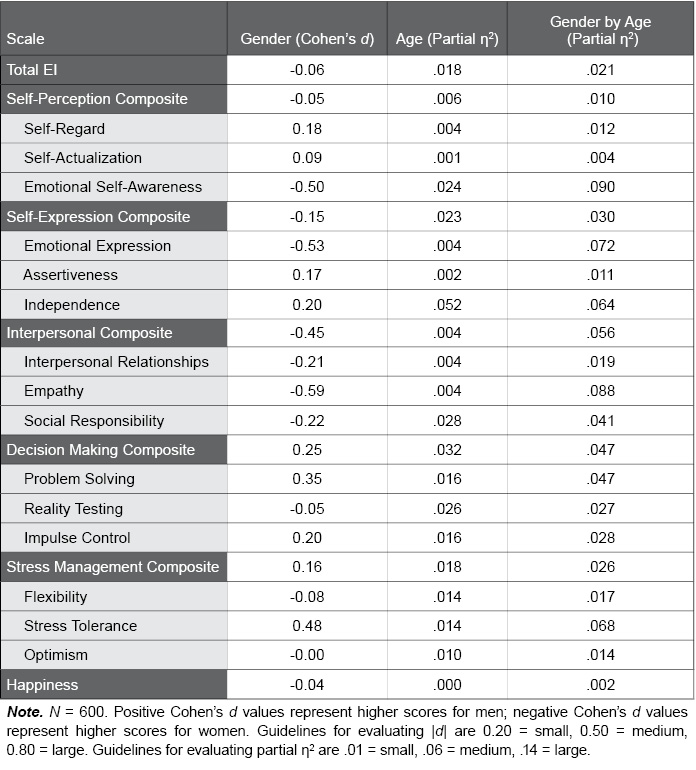
Table J.8. Gender Differences in the EQ-i 2.0 Danish Normative Sample
The following table provides EQ-i 2.0 standard score scale means and standard deviations for men and women in the EQ-i 2.0 Danish normative sample. F and p values convey the statistical significance of gender differences; p values lower than .01, which were found for several scales, indicate significant differences between men and women.
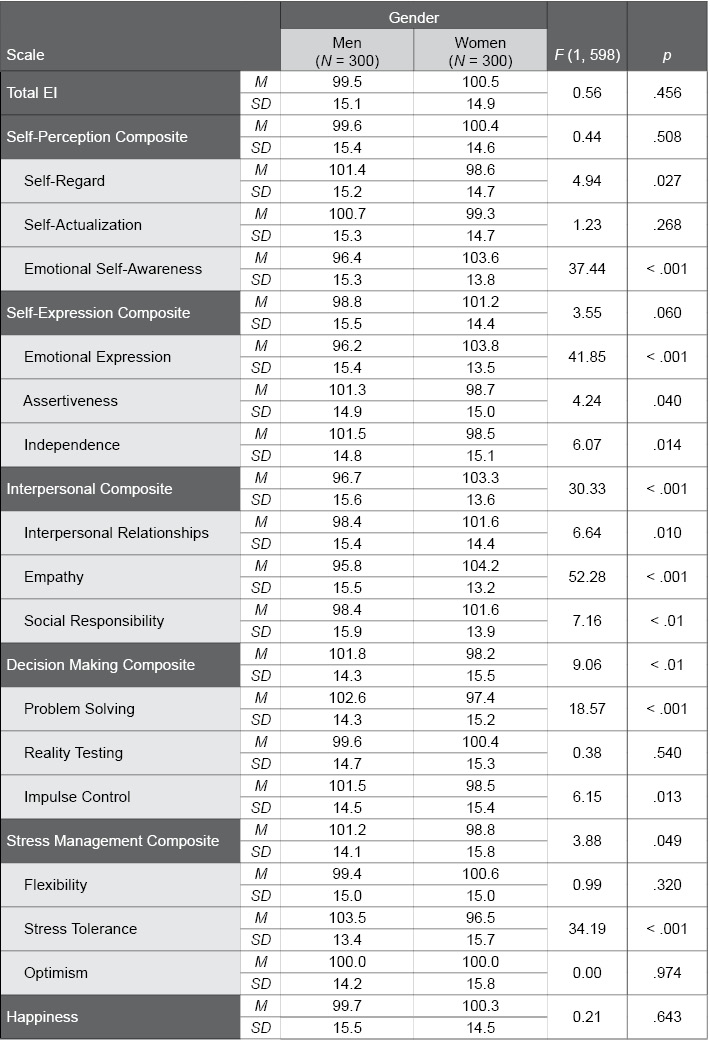
Table J.9. Age Differences in the EQ-i 2.0 Danish Normative Sample
The following table provides EQ-i 2.0 standard score scale means and standard deviations for the various age groups in the EQ-i 2.0 Danish normative sample. F and p values convey the statistical significance of age differences; p values lower than .01, which were found for many scales, suggest significant differences among the age groups.
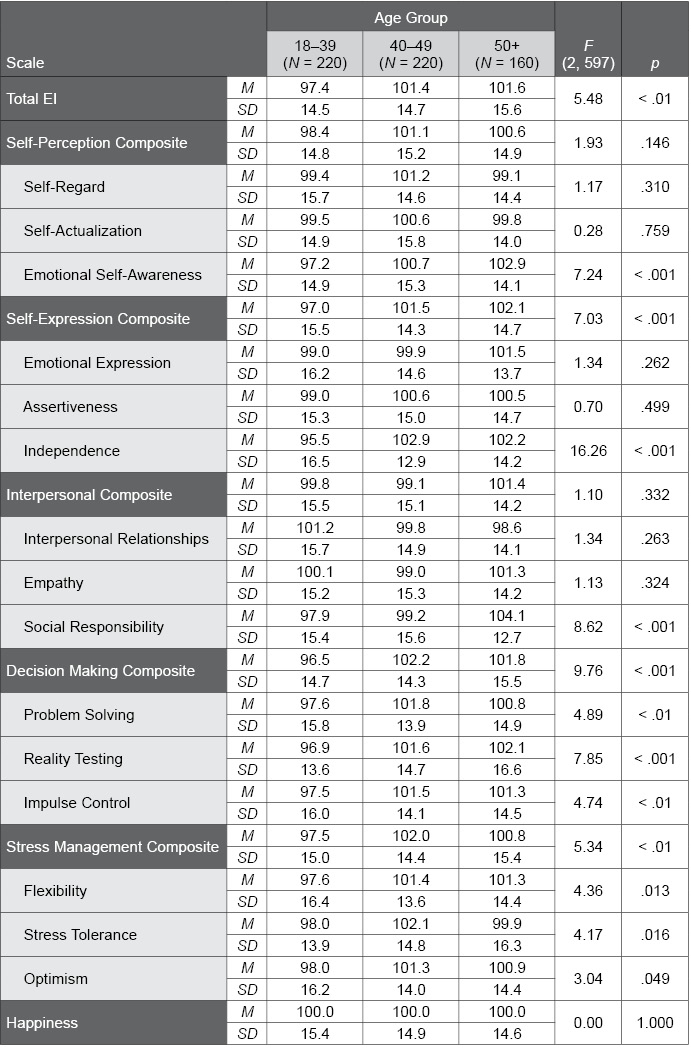
Figure J.1. Histogram of EQ-i 2.0 Total EI Standard Scores in the Danish Normative Sample
This figure illustrates the distribution of EQ-i 2.0 Total EI standard scores in the EQ-i 2.0 Danish normative sample. The distribution of the actual scores approximates the normal “bell-shaped” curve (shown using the black curved line), which suggests that it is unnecessary to apply a normalizing transformation to the scores. Distributions for most other composite scales and subscales show a similar pattern, some with a slight negative skew.
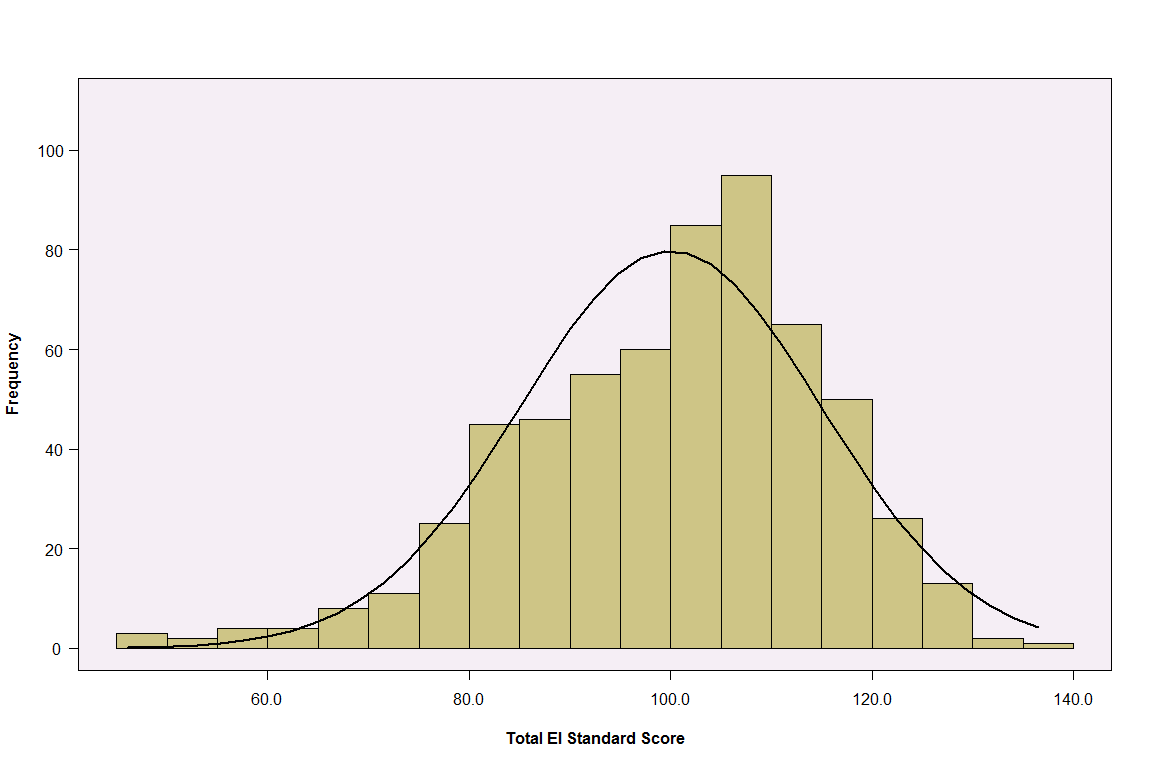
Table J.10. Internal Consistency of EQ-i 2.0 Scales in the Danish Normative Sample
The following table summarizes the internal consistency (Cronbach’s alpha) values for the EQ-i 2.0 scales in the EQ-i 2.0 Danish normative sample, presented overall and separately by gender and age norm group. Alpha values range from 0.00 to 1.00, with high values providing evidence for the strong reliability of the EQ-i 2.0.
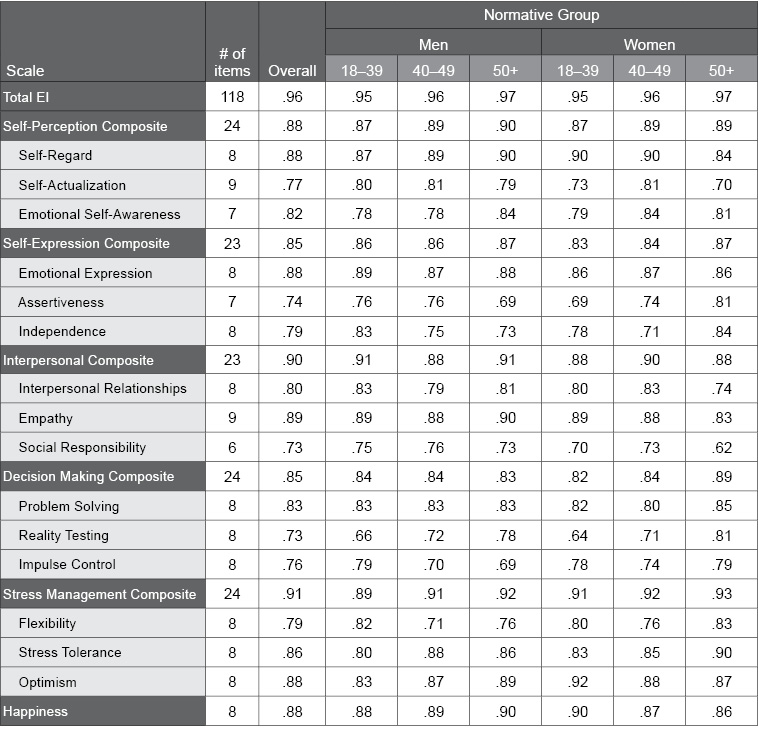
Table J.11. Correlations Among EQ-i 2.0 Composite Scales in the Danish Normative Sample
The following table illustrates the correlations among the EQ-i 2.0 composite scales in the EQ-i 2.0 Danish normative sample. The correlations seen here range from .28 to .70, with higher values suggesting the scales are more interrelated and measure a common construct (i.e., emotional intelligence). Very high values (e.g., > .90) suggest a unidimensional factor structure. Moderate to large correlations, like those found in the Danish normative sample, support both the concept that the scales measure an underlying common construct, as well as the multidimensional factor structure of the EQ-i 2.0.
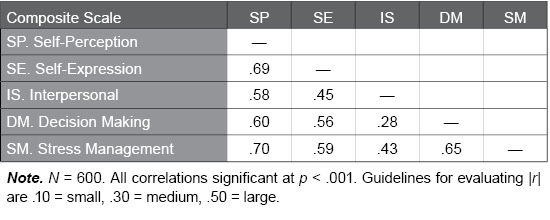
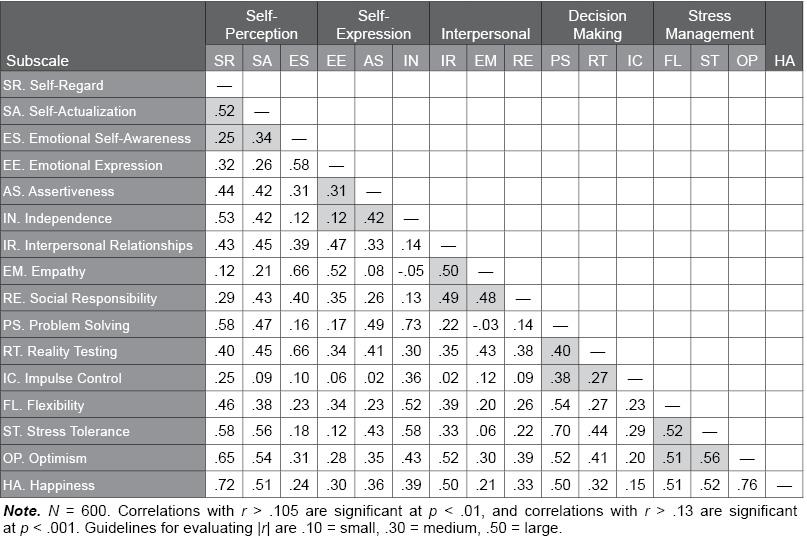
Table J.12. Correlations Among EQ-i 2.0 Subscales in the Danish Normative Sample
The following table illustrates the correlations among the EQ-i 2.0 subscales in the EQ-i 2.0 Danish normative sample. The correlations seen here range from |r| = .02 to .76, with higher values suggesting the scales share a relevant common psychological characteristic. Shaded cells indicate correlations between subscales within the same composite scale. For the most part, moderate to large correlations were found within the composite scales, supporting the multidimensional factor structure of the EQ-i 2.0.